rotator cuff tear diagnostic tests|complete rotator cuff tear test : tv shopping If you have pain in your shoulder or can’t lift your arm, you might have a rotator cuff tear. Beyond googling your symptoms and self-diagnosing, consider trying a few of the special tests we PTs use in the clinic to assess a rotator cuff tear. Even if your pipette tips themselves aren’t contaminated, they are a super-duper .
{plog:ftitle_list}
I think it's important to keep everything sterile and not contaminate your stocks, so I would always autoclave at least before you pippette out into tubes. It can take considerable .Autoclave: Autoclaving is widely recognized as the most effective method for disinfecting lab coats, as it eliminates bacteria, viruses, and spores. To properly autoclave a lab coat, securely seal it in an autoclave bag and .
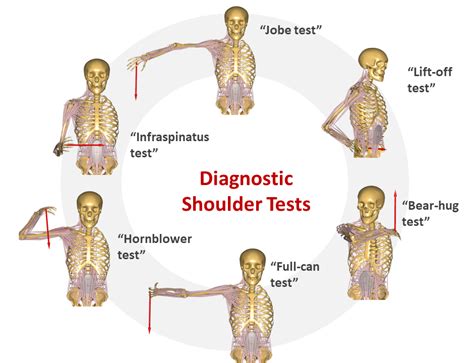
Below are 5 easy Physical Therapy tests you can use to identify whether your rotator cuff is compromised or torn. If have someone else at home capable of following simple directions, ask them to help you by applying oppositional force. Otherwise, if you’re home alone, no worries – you can just use . See moreSo to review, I recommend the following tests for a rotator cuff tear: 1. Empty Can Test 2. Drop Arm Test 3. Lag Sign 4. Infraspinatus Test 5. Lift-Off Test If you . See morePhysical Therapists conduct special tests as part of their overall assessment. Before provoking symptoms with orthopedic tests, your PT will gather as much . See moreA doctor or physiotherapist can use one of more than 25 functional tests during a physical exam to diagnosis a torn rotator cuff. Some of these tests directly indicate a rotator cuff.
If you have pain in your shoulder or can’t lift your arm, you might have a rotator cuff tear. Beyond googling your symptoms and self-diagnosing, consider trying a few of the special tests we PTs use in the clinic to assess a rotator cuff tear. A doctor or physiotherapist can use one of more than 25 functional tests during a physical exam to diagnosis a torn rotator cuff. Some of these tests directly indicate a rotator cuff. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential causes for your pain — such as arthritis. Ultrasound. This type of test uses sound waves to produce images of structures within your body, particularly soft tissues such as muscles and tendons. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder.
The diagnosis of a rotator cuff tear can be established by a careful history and a structured physical examination. The physical examination should include inspection and palpation, range of motion testing, strength testing and special tests. Rotator Cuff Tear. A partial or complete rotator cuff tear makes it difficult to raise and move your arm. You may have shoulder pain and arm weakness. Rotator cuff injuries are common, especially as you get older. Rest, pain relievers and physical therapy can help. The etiology, presentation, and diagnosis of rotator cuff tears will be reviewed here. The treatment of rotator cuff tears, rotator cuff tendinopathy, the shoulder examination, and the general management of patients with shoulder pain are discussed separately.Your doctor may recommend a diagnostic imaging study such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment of a rotator cuff tear may prevent symptoms such as loss of strength and loss of motion from setting in.
A rotator cuff tear diagnosed involves a thorough medical history review, symptom discussion, physical examination, and specific rotator cuff injury tests, with potential imaging to confirm the diagnosis if a tear is suspected. Identifying Symptoms. Diagnosing a rotator cuff injury begins with recognizing key rotator cuff tear symptoms.The current study investigated 8 different clinical tests to determine an optimal testing cluster to differentiate individuals with varying degrees of subacromial impingement secondary to rotator cuff pathology (rotator cuff tear with impingement). If you have pain in your shoulder or can’t lift your arm, you might have a rotator cuff tear. Beyond googling your symptoms and self-diagnosing, consider trying a few of the special tests we PTs use in the clinic to assess a rotator cuff tear.
A doctor or physiotherapist can use one of more than 25 functional tests during a physical exam to diagnosis a torn rotator cuff. Some of these tests directly indicate a rotator cuff.
special test rotator cuff tear
Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential causes for your pain — such as arthritis. Ultrasound. This type of test uses sound waves to produce images of structures within your body, particularly soft tissues such as muscles and tendons. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder.The diagnosis of a rotator cuff tear can be established by a careful history and a structured physical examination. The physical examination should include inspection and palpation, range of motion testing, strength testing and special tests.
Rotator Cuff Tear. A partial or complete rotator cuff tear makes it difficult to raise and move your arm. You may have shoulder pain and arm weakness. Rotator cuff injuries are common, especially as you get older. Rest, pain relievers and physical therapy can help. The etiology, presentation, and diagnosis of rotator cuff tears will be reviewed here. The treatment of rotator cuff tears, rotator cuff tendinopathy, the shoulder examination, and the general management of patients with shoulder pain are discussed separately.Your doctor may recommend a diagnostic imaging study such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment of a rotator cuff tear may prevent symptoms such as loss of strength and loss of motion from setting in. A rotator cuff tear diagnosed involves a thorough medical history review, symptom discussion, physical examination, and specific rotator cuff injury tests, with potential imaging to confirm the diagnosis if a tear is suspected. Identifying Symptoms. Diagnosing a rotator cuff injury begins with recognizing key rotator cuff tear symptoms.
shoulder test for rotator cuff
shoulder rotator cuff tear test
shoulder rotator cuff special tests
Before we explain how long items remain sterile after autoclaving, it is important to understand the sterilisation process that occurs within the autoclave. Autoclaves conduct sterilisation by heating up .
rotator cuff tear diagnostic tests|complete rotator cuff tear test